Machine Learning
Machine learning (ML) is an umbrella term for solving problems for which development of algorithms by human programmers would be cost-prohibitive, and instead the problems are solved by helping machines 'discover' their 'own' algorithms, without needing to be explicitly told what to do by any human-developed algorithms. Recently, generative artificial neural networks have been able to surpass results of many previous approaches. Machine learning approaches have been applied to large language models, computer vision, speech recognition, email filtering, agriculture and medicine, where it is too costly to develop algorithms to perform the needed tasks.
Machine learning (ML) is a field of study in artificial intelligence concerned with the development and study of statistical algorithms that can effectively generalize and thus perform tasks without explicit instructions. Recently, generative artificial neural networks have been able to surpass many previous approaches in performance. Machine learning approaches have been applied to large language models, computer vision, speech recognition, email filtering, agriculture, and medicine, where it is too costly to develop algorithms to perform the needed tasks.
The mathematical foundations of ML are provided by mathematical optimization (mathematical programming) methods. Data mining is a related (parallel) field of study, focusing on exploratory data analysis through unsupervised learning.
Machine Learning
| Unit | Details Contents | Unit | Details Contents |
|---|---|---|---|
| Unit -I | Unit -II | ||
| Unit -III |
|
Unit -IV | |
| Unit -V |
|
Unit -VI | |
| Unit -VII |
|
Unit -VIII |
|
| Unit -IX |
|
Unit -X |
|
INTRODUCTION
ONLINE VIDEOS
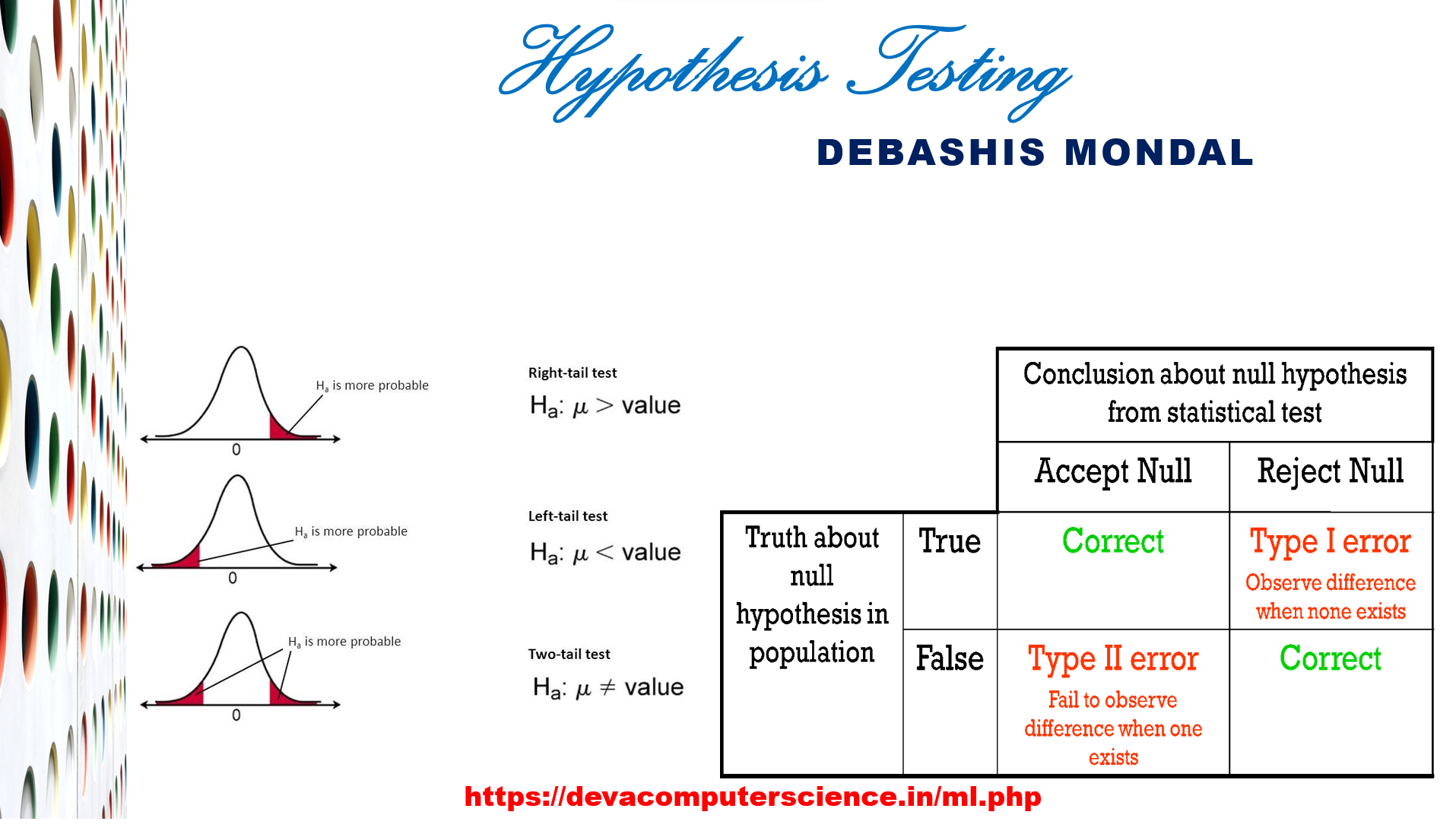
- Statistics for ML
- Python / R for ML
- Data Pre-processing
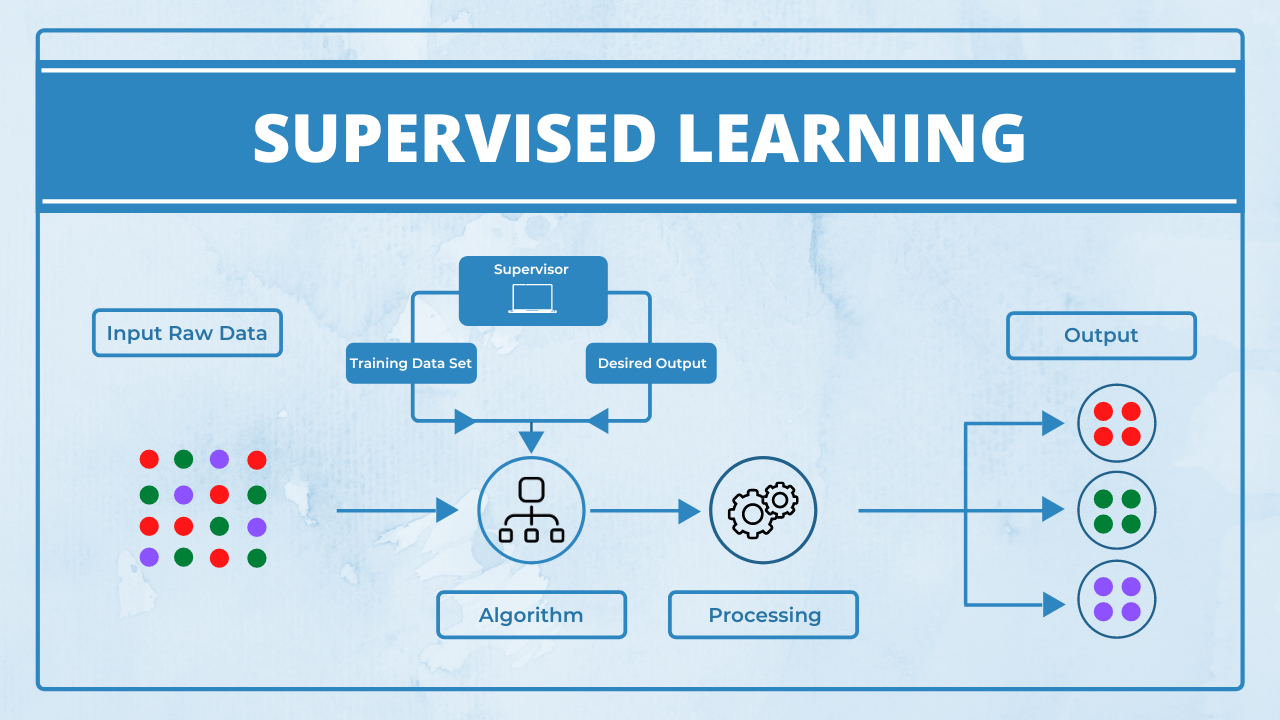
- Supervised Learning
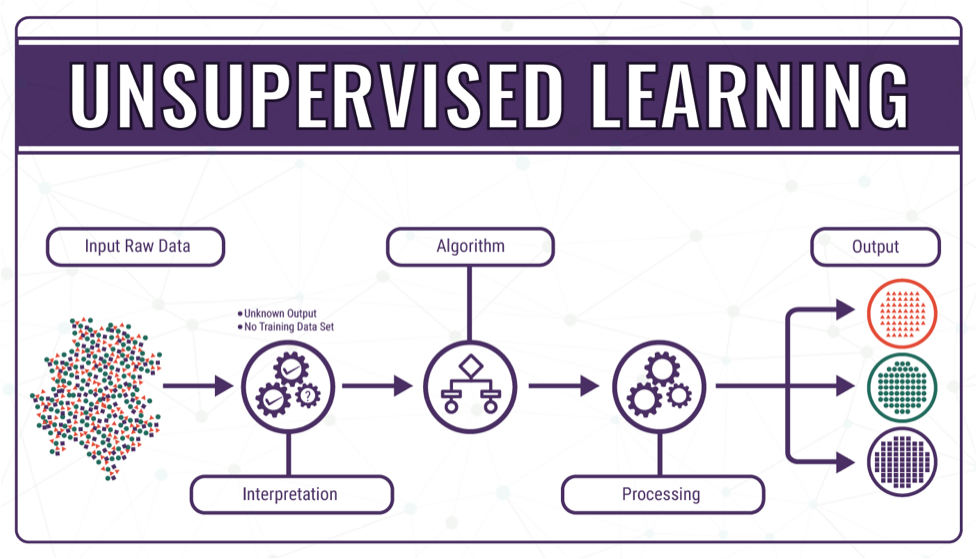
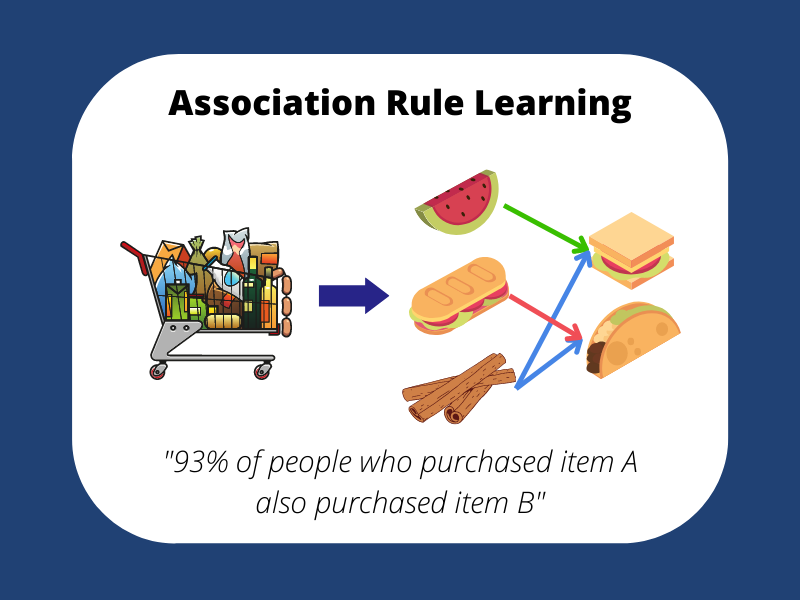
- Unsupervised Learning
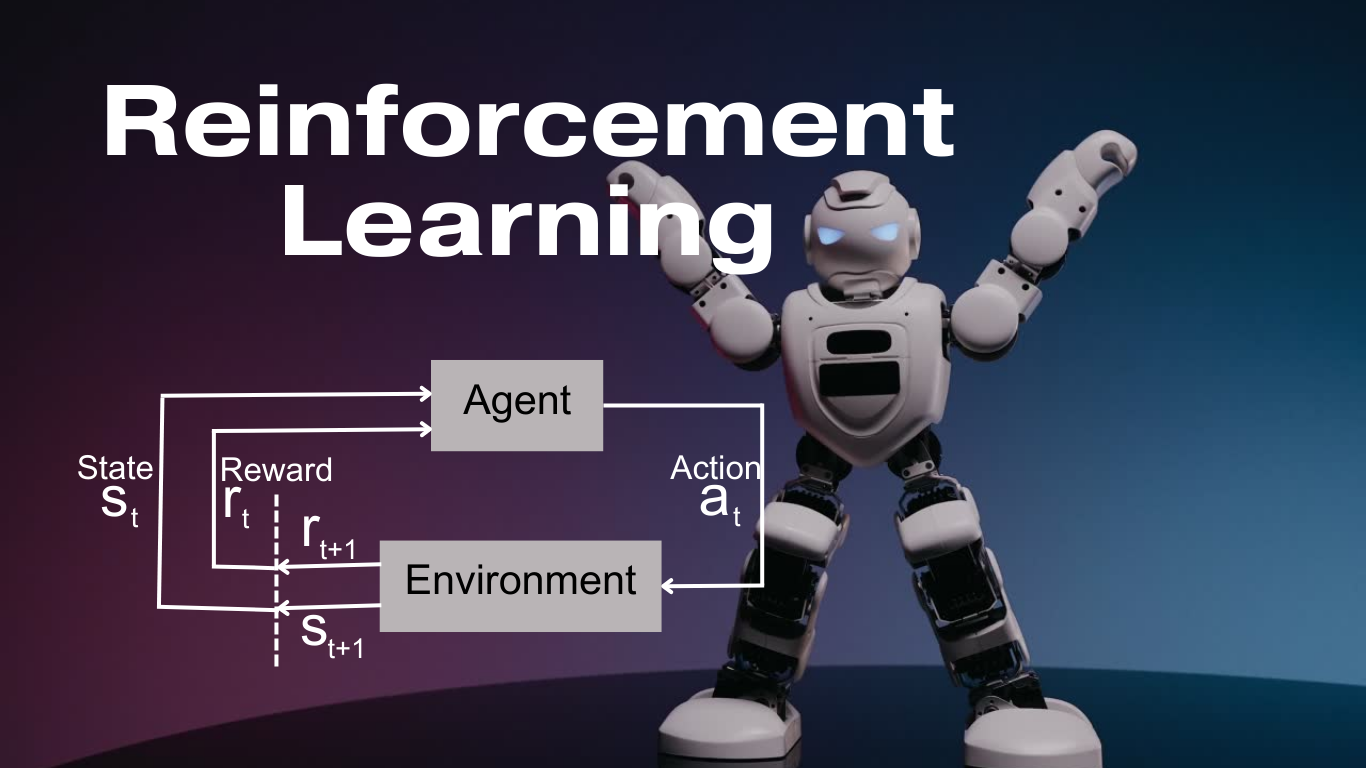
- Reinforcement
 29 Apr 2025
29 Apr 2025

 23 Mar 2023
23 Mar 2023
Weather

 23 Mar 2023
23 Mar 2023
Mail